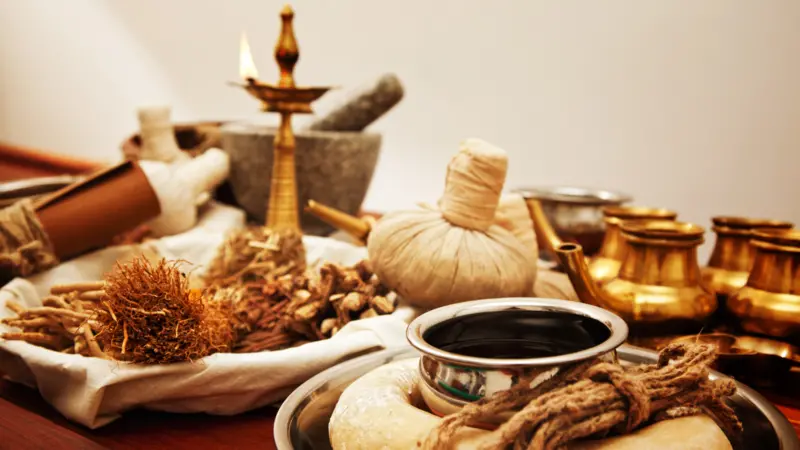
Traditional World Medicine

Traditional World Medicine
WHO Partners with India on Traditional Medicine
In May 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) entered a partnership with India's Ministry of AYUSH. AYUSH is an acronym for Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy, which are the six systems of medicine practiced in India and some neighboring Asian countries. This collaboration aims to integrate traditional Indian medical systems into the global healthcare framework by standardizing and classifying these interventions at an international level.
The WHO-AYUSH collaboration marks a pivotal moment in the global recognition and integration of ancient healing practices with modern healthcare frameworks. It represents more than just documentation; it is a strategic move toward validating traditional medicine on an international platform. By working with WHO, India's traditional medicine systems gain credibility and recognition that could lead to broader acceptance worldwide.
WHO's Traditional Medicine Strategy
The World Health Organization has increasingly recognized the value of traditional medicine systems, having just published a new traditional medicine strategic plan. This strategic plan acknowledges that traditional medicine plays a crucial role in healthcare delivery, particularly in low- and middle- income countries where it may be the primary source of healthcare.
The partnership comes at a time when integrative medicine approaches are gaining popularity worldwide. Many high income countries are exploring ways to incorporate traditional healing practices into their healthcare systems, making standardization increasingly valuable.
Understanding the Partnership
The collaboration focuses on developing educational modules that meet international standards while preserving the authenticity of traditional Indian medicine. These modules will serve multiple purposes: training healthcare professionals, educating patients, and providing standardized information for global health organizations.
The educational module will cover several critical areas:
-
Theoretical Foundations: Comprehensive coverage of the philosophical and theoretical basis of each AYUSH system, including their unique approaches to health and disease.
-
Practical Applications: Detailed guidance on therapeutic practices, diagnostic methods, and treatment protocols specific to each traditional system.
-
Safety Standards: Establishment of safety guidelines and quality control measures to ensure responsible practice of traditional medicine.
-
Integration Protocols: Framework for integrating traditional medicine with conventional healthcare systems in various settings.
Standardization of Traditional Medicine Education
One of the primary benefits of the WHO-AYUSH collaboration is the standardization of traditional medicine education to ensure quality and consistency. Currently, traditional medicine education varies significantly across different institutions and countries.
This standardization will help address several challenges:
-
Quality Assurance: Establishing minimum educational standards for practitioners of traditional Indian medicine.
-
Professional Recognition: Creating pathways for traditional medicine practitioners to gain recognition in formal healthcare systems.
-
Research Integration: Facilitating research collaborations between traditional medicine practitioners and conventional medical researchers. The increased research and standardized research methodologies may help build the evidence base for traditional medicine effectiveness. This research component is crucial for the continued acceptance and integration of traditional medicine into global healthcare systems.
Patient Benefits
The educational modules will emphasize safety protocols and evidence-based practices within traditional medicine systems. This focus on safety is crucial for gaining broader acceptance and integration into mainstream healthcare. Patients will benefit from practitioners who have received standardized training that includes modern safety guidelines, while maintaining the essence of traditional healing approaches.
The standardization is expected to bring multiple benefits: transparent billing and fair pricing for AYUSH services; smoother integration of AYUSH treatments into health insurance coverage; enhanced hospital management and clinical documentation; facilitation of health research involving traditional medicine; and greater global accessibility to AYUSH interventions.
Moving Forward
The implementation will occur in phases, starting with foundational modules and gradually expanding to specialized areas within each AYUSH system. Once developed, these modules will be made available to educational institutions, healthcare organizations, and practitioners worldwide.
As this partnership develops, it may serve as a model for similar collaborations with other traditional medicine systems worldwide. The success of this initiative could pave the way for broader recognition and integration of traditional healing practices into global healthcare frameworks.
The future of healthcare increasingly points toward integrative approaches that honor traditional wisdom while embracing modern scientific rigor. This WHO-AYUSH partnership is a significant step in that direction.
For related articles on this topic, see:
Traditional Medicine Gets Global Recognition from WHO
The World Health Organization has taken a monumental step toward integrating ancient healing practices into modern healthcare systems. At the 78th World Health Assembly, member states approved the WHO Global Traditional Medicine Strategy 2025-2034, marking a watershed moment for traditional medicine practitioners and Indigenous communities worldwide. Read more>>>
China Leads in Integration of Traditional Medicine
In China, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) institutions handle approximately 1.69 billion outpatient visits annually, with TCM departments present in over 90% of general hospitals across the country. China has developed robust regulatory mechanisms to support TCM development while ensuring regulated, safe practices. Read more>>>
REFERENCES
Press Information Bureau. (2025, May 25). India Partners with WHO to Mainstream Ayush Globally through a Landmark Agreement on Traditional Medicine Interventions. Retrieved from https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2131164
MedBound Times. (2025, May 27). India and WHO Collaborate to Integrate Traditional & Global Medicine. Retrieved from https://www.medboundtimes.com/medbound-blog/india-who-collaborate-integrate-traditional-medicine-gl…
Times of India. (2025, May 25). Ayush ministry signs MoU with WHO to create module for traditional Indian medicine. Retrieved from https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/ayush-ministry-signs-mou-with-who-to-create-module-for-tr…
Economic Times. (2025, May 26). India partners with WHO to mainstream Ayush globally through agreement on traditional medicine interventions. Retrieved from https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/india-partners-with-who-to-mainstream-ayush-globall…
Indian Vaidyas. (2025, May 26). Ayush Ministry & WHO Sign MoU to Integrate Traditional Indian Medicine into Global Health System (ICHI). Retrieved from https://indianvaidyas.com/news_details/ayush-ministry-signs-mou-with-who-to-create-module-for-tradi…
Organiser. (2025, May 27). Ayush Goes Global: India’s Historic WHO pact to standardise traditional medicine. Retrieved from https://organiser.org/2025/05/27/294176/bharat/ayush-goes-global-indias-historic-who-pact-to-standa…


 By
By