Chronic Conditions and Diseases

Chronic Conditions and Diseases
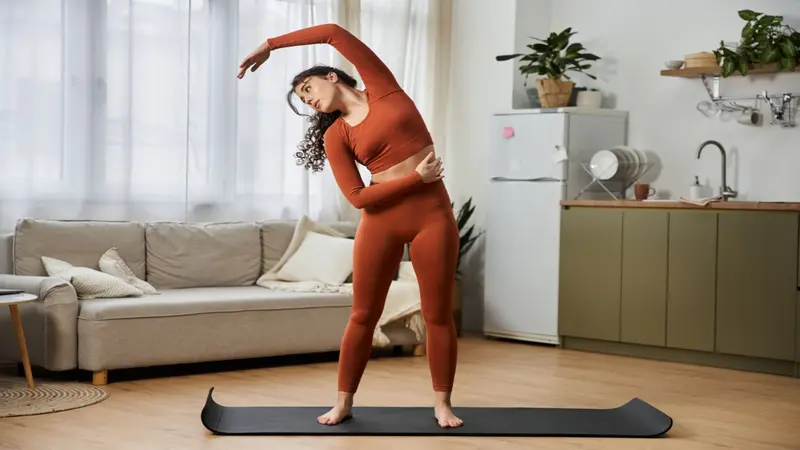
Exercise to Manage Endometriosis Symptoms
Endometriosis is a chronic condition affecting about one in 10 women of reproductive age worldwide. It occurs when tissue biologically similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, often causing pelvic pain, painful periods, painful intercourse and fertility challenges. These symptoms can significantly lower quality of life and may lead to depression, fatigue and reduced work productivity. Current treatments focus mainly on pain relief through medication or surgery, but symptoms often return. Researchers are exploring complementary approaches, including physical activity and exercise, to improve both physical and mental well-being.
In a 2025 meta-analysis published in PloS One, researchers reviewed randomized controlled trials that studied the effects of exercise on women with endometriosis. They included six studies with a total of more than 250 participants. Types of exercise studied included yoga, stretching, aerobic and resistance exercises, virtual-reality workouts and progressive muscle relaxation. Outcomes measured included quality of life, pain, mental health, pelvic floor function and bone density.
The review found that physical activity and exercise had positive effects. Exercise improved quality of life, particularly by reducing pain, increasing a sense of control, and enhancing emotional well-being. Yoga and personalized exercise programs helped reduce daily pelvic pain and improved mental health. Some interventions also helped with pelvic floor function and bone density, especially for women who had received hormone treatments that can weaken bones.
Overall, exercise appears to be a safe and helpful way to manage endometriosis symptoms.
REFERENCES
Xie, M., Qing, X., Huang, H., Zhang, L., Tu, Q., Guo, H., & Zhang, J. (2025). The effectiveness and safety of physical activity and exercise on women with endometriosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS one, 20(2), e0317820. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0317820



 By
By