
Food, Farming and Nutrition

Food, Farming and Nutrition
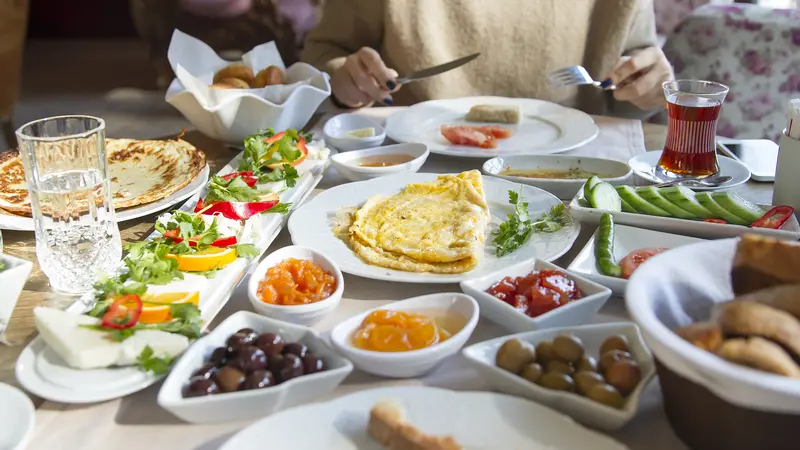
Mediterranean Diet Improves Depression, Study Shows
In a randomized controlled trial out of the University of South Australia, published in the journal Nutritional Neuroscience, participants with depression who followed a Mediterranean-style diet (Med Diet) substantially improved their depression and mental health scores over the study period.
Major depression, which disproportionately affects women, has recently been ranked as the second highest cause of loss of years of life from disability (YLD). According to the Global Burden of Disease, from 1990 to 2013, YLD attributed to depressive disorders increased by 53.4% and cardiovascular disease by 89.2%, constituting tremendous personal, psychosocial, and financial costs.
It has long been known there is a cause and effect between cardiovascular disease and depression. What may be less known is that these conditions share underlying biological risk factors such as inflammation, low levels of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and poor diet. But changing one’s diet is difficult due to ingrained habit and can be especially so for those that are depressed and lack motivation.
A traditional Med Diet consists of a high intake of vegetables, fruit, legumes, nuts, seeds, olives, whole grains, extra-virgin olive oil as the main culinary fat, moderate intake of fish, and low intakes of sweets, red meat, and processed food. Not only has a Med Diet been shown to be protective against cardiovascular disease, but as it is palatable it’s likely to become a sustainable part of a healthy lifestyle.
Researchers divided their study into two groups. All 152 adult participants who began the trial self-reported depression. One group was placed on a Med Diet with periodic social interactions revolving around Med Diet education and cooking classes. The Med Diet group were provided with omega-3 fish oil supplements and free food so they could try their new cooking skills at home. The other group met for social activities such as games with the same frequency as the cooking classes for the Med Diet group.
While both groups exhibited improvements in mental health, the Med Diet group reported significantly greater improvements in depression and overall mental health compared to the social group. The improvements were strongly correlated with improvements in diet, most notably for greater diversity of vegetables and fruit consumed, greater intake of legumes, vegetables, fruit and nuts, and reduced consumption of unhealthy snacks, take-out food, and meat.
Researchers noted that increased take-out and ultra-processed food consumption is not only bad for our health, but it has also eliminated the benefits of growing, cooking, and enjoying good wholesome food together.
REFERENCES
Parletta, N., Zarnowiecki, D., Cho, J., Wilson, A., Bogomolova, S., Villani, A., Itsiopoulos, C., Niyonsenga, T., Blunden, S., Meyer, B., Segal, L., Baune, B. T., & O’Dea. K. (2019). A Mediterranean-style dietary intervention supplemented with fish oil improves diet quality and mental health in people with depression: A randomized controlled trial (HELFIMED). Nutritional Neuroscience, 22(7), 474–487. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2017.1411320


 By
By






